Overview
There have been many products from Microsoft over the years that assisted with update management such as Windows Update, Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) and Windows Update for Business.
Windows Autopatch is a cloud managed service, provided by Microsoft that automates Windows Updates. This includes Windows 10 and 11, Microsoft Edge, Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise and Microsoft Teams.
We all know patching is quite a mundane, and time-consuming task that IT admins must constantly keep on top of if they want to keep their environment secure. Windows Autopatch can help alleviate this by managing lots of the work for you, delivering updates to registered devices, therefore freeing up time and minimising disruption to end users.
Security is a big talking point right now and by keeping software up to date, there are fewer threats and vulnerabilities to the devices on your network.
Key highlights of Windows Autopatch include:
- Enhancing security: By keeping software current, Windows Autopatch reduces vulnerabilities and threats to devices.
- Boosting productivity: Users gain access to the latest tools and features, enabling them to enhance collaboration and creation.
- Streamlining IT admin tasks: By automating routine endpoint updates, Windows Autopatch allows IT professionals to focus on value-adding activities.
- Cloud-based updates: Organizations can reduce their investment in on-premises hardware as updates are delivered from the cloud.
- Minimising disruptions: Windows Autopatch adopts a sequential deployment approach via deployment rings and considers reliability and compatibility signals to minimise disruptions caused by updates.
The service has grown over the past couple of years, and continues to be a key tool for automating updates.
Prerequisites
- Windows Autopatch is part of the enterprise licensing packages (Windows 10/11 Enterprise E3 or higher), so if you have these licenses then you already have this service. You can find more information on licensing here: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/deployment/windows-autopatch/prepare/windows-autopatch-prerequisites#more-about-licenses
- Your user accounts must either be synched from on-premises Active Directory to Azure Active Directory or Azure Active Directory must be the source of authority for all your user accounts.
- Last of all, as this is an Intune service, the devices must be enrolled into Intune and Intune must be the MDM authority.
Rings
The deployment of updates are delivered using rings in the standard Microsoft fashion. Windows Autopatch can automatically detect variations in an environment and create the four rings dynamically.
Deployment Rings
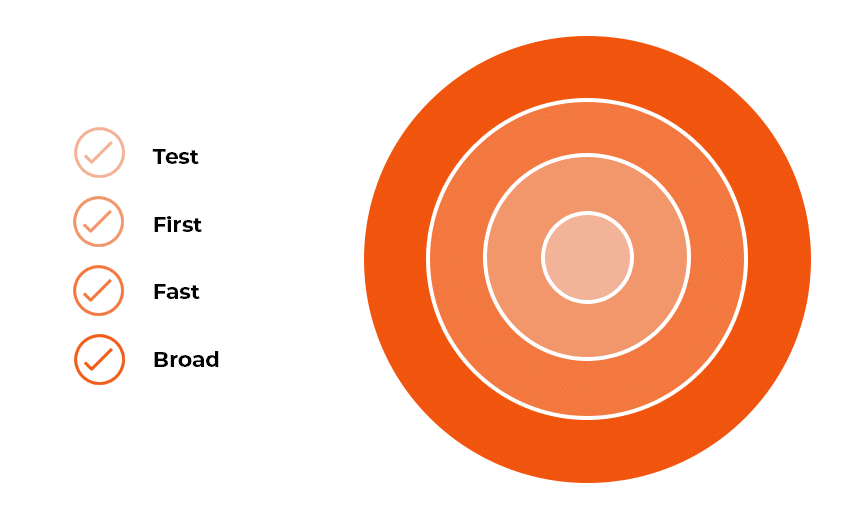
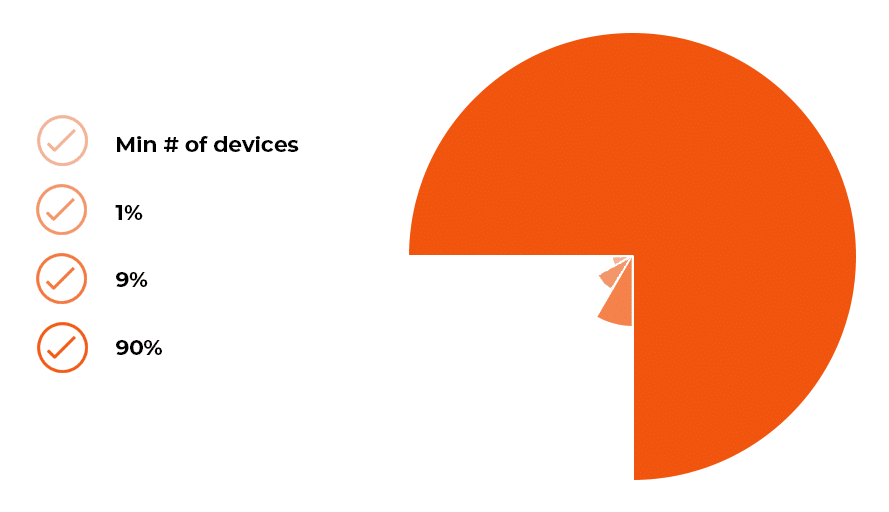
While the diagram above is useful for understanding the relationships of testing rings, the below shows the difference in ring population size. The ‘test ring’ contains a minimum number of representative devices. The ‘first’ ring contains around 1% of all devices being managed. The ‘fast’ ring contains about 9% of devices, and the rest are assigned to the ‘broad’ ring. All the devices can be manually moved from one group to another.
Ring Groups
What is the difference between Windows Update for Business and Windows Autopatch?
I’ve put together a comparison list of some topics of interest.
Update Management Approach:
- Windows Update for Business: It provides IT administrators with tools to manage the deployment and timing of updates. Administrators can create deployment rings, specify maintenance windows, and control the distribution of updates.
- Windows Autopatch: It is a service that removes the need for organizations to plan and operate the update process. Windows Autopatch shifts the burden of update management from the IT department to Microsoft. It utilises Windows Update for Business and other service components to update devices, whilst still allowing control.
Operational Responsibility:
- Windows Update for Business: IT administrators are responsible for planning and implementing update deployment strategies and managing the update process within their organization.
- Windows Autopatch: The update process is managed by Microsoft. It moves the responsibility of update planning and operation from the IT department to Microsoft, reducing the operational burden on organizations.
Device Enrolment:
- Windows Update for Business: Organizations can enrol their devices into Windows Update for Business to gain additional control over the update process.
- Windows Autopatch: Devices are enrolled in Windows Autopatch, which leverages Windows Update for Business and other service components. Autopatch handles the update process, and individual device-level control is not supported.
Support for Cloud PCs:
- Windows Update for Business: It supports Cloud PCs, allowing administrators to manage updates for virtual desktops.
- Windows Autopatch: It supports Cloud PCs and provides the same update management capabilities for virtual desktops as it does for physical devices.
Feature Updates:
- Windows Update for Business: Administrators can control the deployment of feature updates, specifying the timing and pace of rollout within their organization.
- Windows Autopatch: Autopatch manages all aspects of feature update deployment, including the rollout process from test rings to broad rings. The decision of when to move to the next ring is handled by Autopatch and is not customer configurable, although rings can be delayed if an issue occurs.
Deployment Flexibility:
- Windows Update for Business: It offers more flexibility in terms of customisation and control over update deployment strategies, allowing organizations to define their own deployment rings and maintenance windows.
- Windows Autopatch: It simplifies the update process by removing the need for complex customisation. Autopatch provides a streamlined and automated approach to update management.
In summary, while Windows Update for Business provides more customisation options and control, Windows Autopatch offers a simplified and automated approach to update management, reducing the operational burden on organizations.
AUTOPATCH GROUPS – UPDATED
You can now use Groups with Autopatch!
Windows Autopatch Groups are logical containers that group several Microsoft Entra groups and software update policies. These groups help replicate your organisational structure and manage updates according to your specific deployment cadence.
Key Benefits
- Replicating Organisational Structure
- Autopatch Groups can mirror your existing device-based Microsoft Entra group targeting logic, ensuring updates are managed in a way that aligns with your organisational setup
- Flexible Deployment Rings
- You can create up to 15 deployment rings per Autopatch Group, allowing for detailed control over how updates are rolled out across different segments of your organisation
- Custom Device Assignment
- Decide which devices belong to which deployment rings during the setup process. This flexibility ensures that critical devices can be tested first, while less critical devices can be updated later
- Custom Deployment Cadence
- Choose the update deployment cadence that best fits your business needs. This can help minimise disruptions and ensure updates are applied at the most convenient times
Summary
I hope this has been useful and shed some light on a fairly new product that some people might not have much information on right now. It also ties in with my Ultimate guide to Intune blog.
If you require any more information, please get in touch.